17.5.2019. Automated Driving levels 3 and 4, a 48-Volt drive system and a platform for E-vehicles – Volkswagen shows on the 40. Vienna motor Symposium the way to a networked and CO₂-neutral mobility.
An important contribution to sustainable mobility, the Mild Hybrid (mHEV)-System. Depending on driving style, a quantity of fuel of approximately 0.4 litres can be saved per 100 kilometres and CO₂ emissions are reduced. In addition, Volkswagen is for the first time, accurate insight into the MEB (Modular E-drive modular system), which will create the conditions for Autonomous Driving.
“We want to offer every customer the mobility, which he expected. And in any market, the mobility that is needed. Therefore, we continue in our drive strategy in a broad Mix of technologies,“ explains Dr. Frank Welsch, a member of the brand Board of management. He wants to hold today, Wednesday, the opening speech in Vienna’s Hofburg Palace. “The drive portfolio extends from part of electrified powertrains, such as the mHEV to fully electrified vehicles on the Basis of our newly developed E-platform MEB.”
With the 48-Volt Mild Hybrid (mHEV) in combination with the petrol engine 1.5 l TSI evo, Volkswagen is launching the next hybridization step in his drives. The conventional 12-Volt on-Board network is supplemented with a 48-Volt power supply. With this tension of the belt starter generator (RSG), which has its place at the place of the alternator in addition to engine operates.
He dominated two main operating conditions: recuperation and Boost. During the recuperation, the RSG acts as a Generator that can absorb part of the kinetic energy of the vehicle. The recuperation energy is stored as electrical energy in a separate 48-Volt-Lithium-ion battery, which is disposed below the passenger seat. When Boosting, this energy is used by the RSG to drive and to support the TSI. Other smart features of the RSG in support of the TSI engine, during the starting process, where it takes on the function of the starter Pinion. In doing so, he saves fuel, and makes the starting process more comfortable.
The already well-known coasting with engine-Off function of the mHEV offers as well. This operating mode lets the vehicle when the engine is off completely emission-free “sailing”, which contributes significantly to the reduction in fuel consumption of 0.4 liters/100 km. A link between the 48-Volt power supply and the rest of the vehicle’s electrical system is a DC/DC Converter transforms the 48 in 12 Volt.
The most efficient method to reduce CO₂ emissions, lake Volkswagen in the massive Expansion of the battery-electric drive (BEV). The Basis for The electric cars of the next Generation of the MDS. Its essential features are the space-saving under-floor-volt battery, the compact E built-in High-drive at the rear and optionally front axle, as well as the standard CCS-loading system for quick Loading. He is also the Basis for the newly developed End-to-End electronics architecture, “E3”, and the operating system “vw.OS“, new mobility services and driver assistance systems can be established. Thus, Volkswagen has developed from a pure vehicle manufacturer to mobility provider and creates To in addition, the requirements for automated.
How much development work for the large-scale industrialization of E-drives Volkswagen has done, shows an example of a primary drive of the MDBs on the rear axle. “Here, a permanently excited synchronous machine is used, the high power density, high efficiency and performance, constancy over a wide speed range of 16,000 1/min, is characterized,” explains Karsten Bennewitz, head of development of Hybrid and electric drives. The first vehicle on the Basis of the MEB of the ID.3
. With a range of 330 to about 550 km (WLTP), a power of 150 kW and a maximum speed of 160 km/h he will allow locally emission-free Driving.
For over 20 years, Volkswagen developed assisted functions, and now offers under the umbrella brand IQ.DRIVE a wide range of driver assistance systems for the vehicle longitudinal and vehicle transverse guidance. For these systems, the precursor form on the way to automated and, ultimately, driverless Driving. In the future, Autonomous vehicles will. participate actively on the road, in various domains, such as the highway or the car Park The drivers are gradually removed more and more tasks by the vehicle.
In particular, the jump from today, already available, semi-automated Level 2 the following Level 3 and 4 presents a particular technical, but also legal and ethical challenge. The reason for this in these Levels for the first time is – at least temporarily Handing the responsibility for the execution of the driving task from the driver to the automatic driving function.

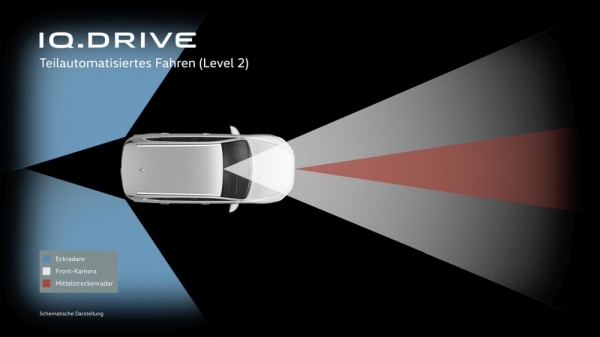
Volkswagen IQ-DRIVE – Sensor system for level 2 (photo: Volkswagen AG)